
LATTICE ENERGY EQUATION KE FULL
Determining the energy required to convert a gaseous atom into an ion with a full shell of electrons – Electron affinity.Determining the energy required to remove an electron from a gaseous atom to form a cation – Ionization energy.The Born-Haber cycle is a multi-step process that involves the following:
LATTICE ENERGY EQUATION KE SERIES
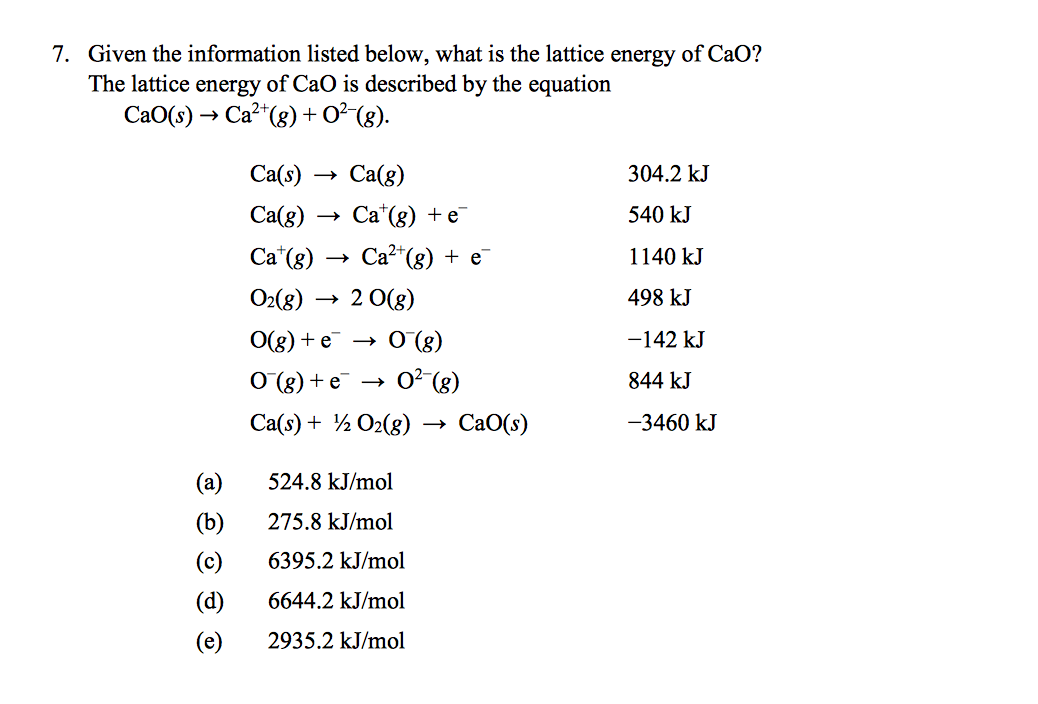
The Born-Haber cycle method includes a series of steps that begin with the elements in their standard states and ends with the formation of the ionic compound. There are a couple of methods to calculate lattice energy, but the Born-Haber cycle method is the most common. Now that we have a basic understanding of lattice energy, let's get into the nitty-gritty of calculating it. The lattice energy is denoted by U, and it is a measure of the strength of the attractive forces between the ions in a crystal lattice. To break it down even further, lattice energy is the energy required to convert a solid ionic compound into isolated gaseous ions, which is represented by the equation: It is essentially the energy that is released or absorbed when a crystal lattice is formed from gaseous ions. Lattice energy is the total energy required to break apart an ionic solid and separate its constituent ions.
LATTICE ENERGY EQUATION KE HOW TO
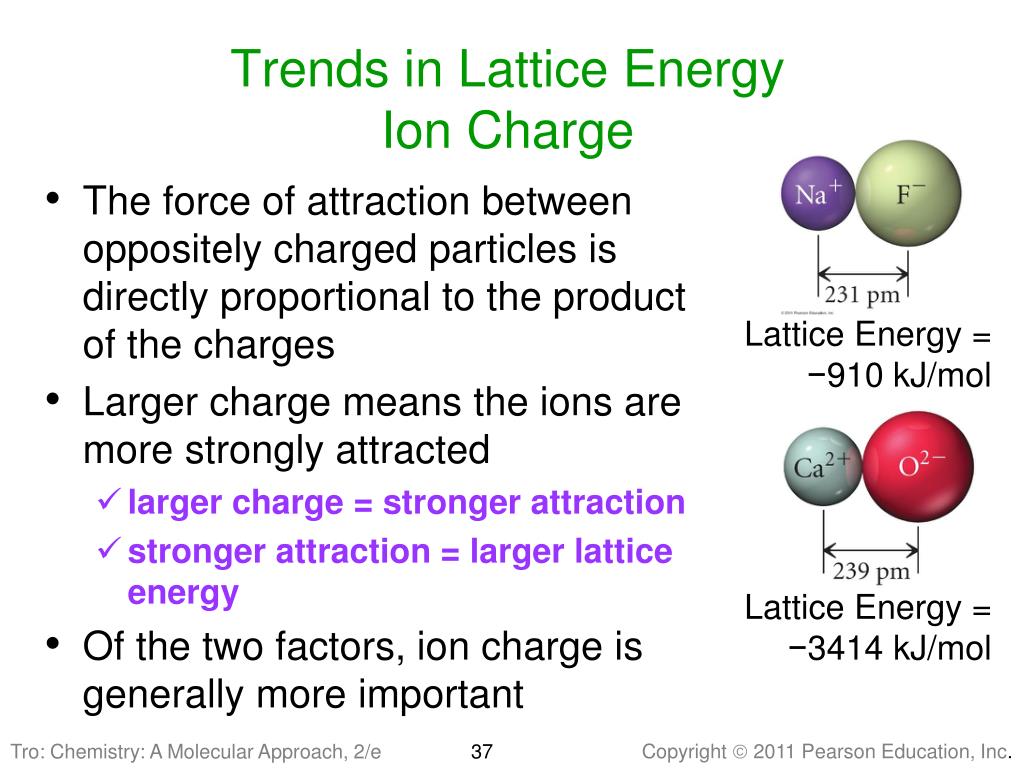
Lattice energies are large when ions are closer together, the distance between the ions is small and when the charges are larger. Coulomb’s law is equal to a constant, k, multiplied by the product of the ion charges, z 1 and z 22, between the ions.


Recall, lattice energy is positive meaning it is endothermic. The stronger the bond, the higher the lattice energy. Lattice energy, E lattice is dependent on the strength of the bond between the cation and anion in an ionic bond. The lattice energy is always positive, because it takes energy to separate the ions from the solid. The equation for the lattice energy is the reverse of the equation in Step 5 in the figure below, for the formation of the solid from its ions which releases 787 kJ/mol of energy.Ī Born-Haber cycle allows the calculation of the lattice energy for a solid ionic compound. The process absorbs energy, and is highly endothermic. Lattice energy, E lattice is the energy required to separate one mole of a solid ionic compound into its gaseous ions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
